链路层 Direct Link Networks¶
Link Layer Overview¶
- Link Layer Service
- Framing
- Link access
- Reliable delivery
- Error detection and correction
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Token
广播信道的 4 种希望的特性: 1. 当仅有一个节点发送数据时候,该节点有 \(R\) bps 的吞吐量 2. 当有 \(M\) 个节点发送数据时,每个节点吞吐量为 \(R/M\) bps。这不必要求 \(M\) 个节点中的每一个节点总有 \(R/M\) 的瞬间速率。 3. 协议是去中心化的。(不会主节点故障就整个系统崩溃) 4. 协议是简单的,实现不昂贵。
Handling Multiple Access¶
这里介绍几个不同的协议和方案,来解决 Multiple Access 方案
Channel Partitioning¶
TDMA¶
- TDMA: time division multiple access
- Access to channel in "slots and rounds"
- Each station get fixed length slot (packet trans time)
- Unused slots go idle
CDMA¶
- CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access
- All nodes share same frequency, but each node has own "chipping" sequence (i.e., code set) to encode data
- (本质是一组线性空间的正交基,发送方用这些基编码,接收方再解码,利用线性代数的方法)
- If codes are "orthogonal"
- Multiple nodes can transmit simultaneously with minimal interference
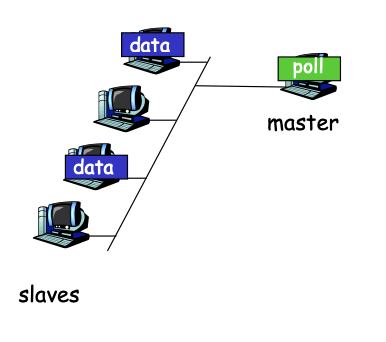
Taking Turns (轮询协议)¶
- Polling
- Master node "invites" slave nodes to transmit in turn.
- (主仆关系,一个个排队发)
- Typically used with "dump" salve devices
- Master node "invites" slave nodes to transmit in turn.
Token passing(令牌传递协议)¶
- Control token (令牌)passed from one node to next sequentially
- Token to message
- 这种协议没有主节点,令牌按固定的次序进行交换
- 一个节点收到令牌的时候
- 仅当它有帧要发送,才持有这个令牌 token
- 并发送最大数目的帧数,将令牌传递。
- 否则,它将立刻转发令牌给下一个节点。 令牌传递协议是分散的,但是会因为某个节点的故障而崩溃。
- 仅当它有帧要发送,才持有这个令牌 token
Random Access¶
Random Access Protocols¶
- 什么时候节点有包要发 (has packet to send)
- Transmit at full channel data rate \(R\)
- No priori coordination among nodes
- Two or more transmitting nodes \(\to\) collision
- Random access MAC protocol specifies:
- How to detect / avoid collisions
- How to recover from collisions
- Examples of random access MAC
- ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA
- CSMA, CSMA/CD, CSMA/CA
- 后面都有介绍
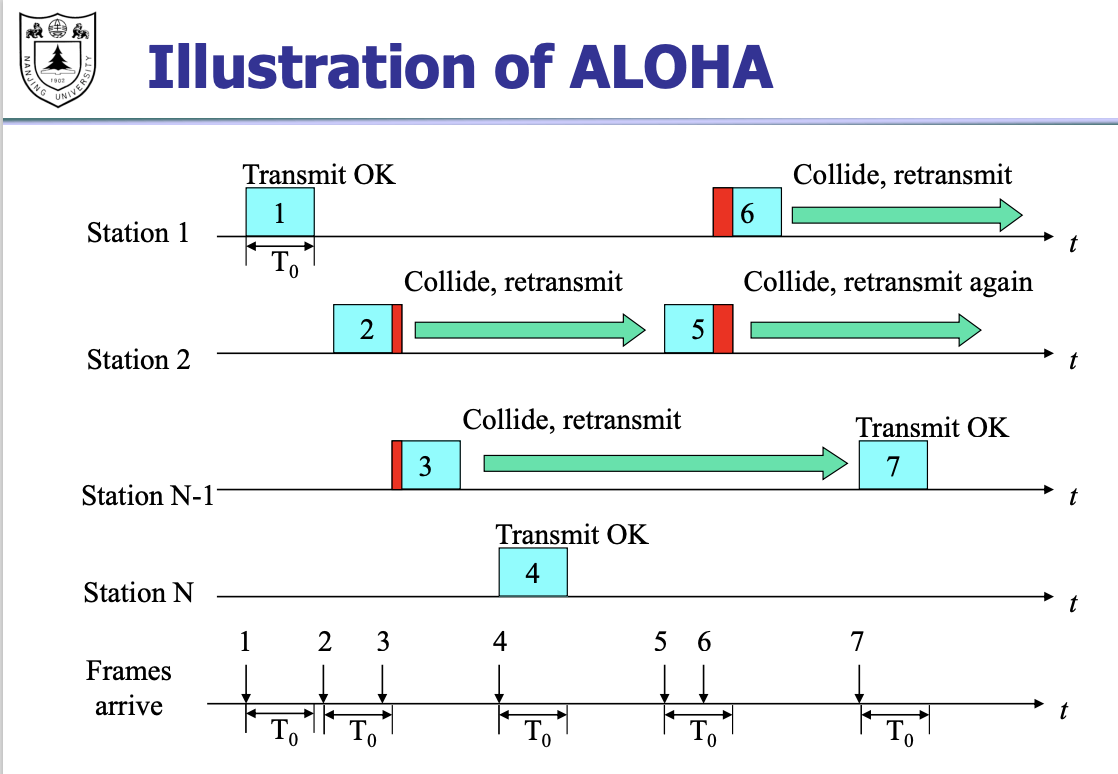
例子:ALOHA 传输¶
that is : Additive Link On-line HAwaii system
最早的:纯ALOHA¶
纯ALOHA 实现非常简单: - 当一帧首次到达(即一个网络层数据报 datagram 从网络层传递下来),节点立刻将该帧传入广播信道。 - 如果一个传输的帧经历了与别的传输的碰撞, - 它将立刻以概率\(p\) 重传, - 或者以概率 \(1-p\) 在另一个帧时间内等待
由于当某节点开始传输时,其他所有节点不能传输;事件 \(A\) 能传输概率为 \(p(1-p)^{N-1}\) 且其他所有节点都不传输的情况下,某节点才能传输。事件 \(B\) 的概率同样为 \(p(1-p)^{N-1}\) 所以总体概率为 \(p(1-p)^{2(N-1)}\)
时隙ALOHA 效率分析¶
- 时隙 ALOHA 是一种随机接入访问协议。它在相同时隙的间隔内发送分组,若侦测到碰撞,那么选一个随机等待时间然后继续重传。
- 效率分析
- a. 当有 \(N\) 个活跃节点的时候,时隙 ALOHA 的效率是 \(Np(1-p)^{N-1}\)。求出使这个表达式最大化的 \(p\) 值
- 求导,得到一阶条件 $$ N(1-p){N-1}-Np\cdot(N-1)(1-p){N-2}=0 $$
- 得到 \(1-p-pN+p=0\), 则 \(p=\dfrac{1}{N}\)
- b.
- 令 \(N\) 趋近于无穷,得到效率 $$ N\times \frac{1}{N}\left( 1-\frac{1}{N} \right)^{N-1}=\frac{1}{e} $$
机制:
- Sender
- When station has frame, it sends
- If ACK, fine
- if not, retransmit with probability p, and wait with probability 1-p
- if no ACK after retransmissions, give up
- Receiver
- Use frame check sequence
- If frame OK and address matches receiver, send ACK
- Frame may be damaged by noise or collision
- Another station transmitting at the same time
- Any overlap (重叠的) of frames causes collision
### CSMA - Carrier sense multiple access (载波侦听多路访问) - CSMA: listen before transmit (人类行为:不要打扰别人) - if channel sensed idle: transmit entire frame - if channel sensed busy, defer transmisstion - 无法避免碰撞: - Hint: Propagation delay - 信息在链路上传输,存在传播时延
Non-persistent CSMA¶
- Station wishing to transmit
listens- if medium is idle, transmit; otherwise, go to 2
- if busy, wait amount of random time (delay) and repeat 1
- Random delays reduces probability of collisions
- Two stations waiting will take different time to begin transmission
- Capacity is wasted, since medium will remain idle following end of transmission
- Even if one or more stations waiting
- Non-persistent stations are deferential (毕恭毕敬的)
但是这个“先听再发”,会浪费一定的带宽。所以有 1-persist CSMA
1 -Persistent CSMA¶
- To avoid idle channel time, 1-persistent protocol used
- Station wishing to transmit listens
- If medium idle, transmit; otherwise, goto step 2
- If medium busy, listen until idle; then transmit immediately
- 1-persistent stations selfish
- If two or more stations waiting, collision guaranteed
CSMA/CD (CSMA with Collision Detection)¶
总结运行如下
1. 从网络层获得 datagram,准备链路层帧,放入帧适配器
2. 无别的适配器的能量(信道空闲)就传输
3. 传输过程监控:(Detection 之谓)
1. 如果别的适配器发信号,就停止,goto 5
4. 如果传完了都没有被停止,适配器就完成了该帧。
5. 如果接收到了来自其他适配器的信号能量,send jam signal then abort (发送 jam signal,大小为 48 比特)
6. 终止传输后,适配器等待一个 随机时间量,然后返回步骤 2
这个随机时间量非常重要。 如果两个节点同时开始传输,发生碰撞后,如果等待同一个时间开始重传,将持续碰撞。所以选择随机量
最小帧长¶
由于 CSMA 要求在传输 datagram 的同时检测冲突,所以这就对我们传输的帧大小有一定要求,即我们传输的帧不能太小,以至于在其传输(transport)完毕之前,我们来不及检测到链路冲突(即链路上传播遇到了冲突,但是我们已经传完了来不及触发重传等处理机制)
- 为了确保发送设备有足够的时间检测碰撞,帧的长度必须大于信号传播一圈的时间(RTT,Round Trip Time)。
- 信号传播速度和距离:
- 以太网最大网段长度为500米,每个网段之间可以通过中继器连接,总长度不超过5个网段(大约2500米)。电信号在铜线中的传播速度约为光速的
2/3,即 \(\approx 2\times10^{8} 米/秒。\)
- 以太网最大网段长度为500米,每个网段之间可以通过中继器连接,总长度不超过5个网段(大约2500米)。电信号在铜线中的传播速度约为光速的
- 以太网的传输速率:
- 经典以太网速率为10 Mbps,发送1比特需要
1/10*10^6秒
- 经典以太网速率为10 Mbps,发送1比特需要
- 计算最小帧长:
- 假设信号需要传播最远距离(2500米),往返时间 \(t_{RTT} \approx \frac{2\times 2500}{2\times 10 ^8}=25\mu s\)
- 在此时间内,网络设备至少需要发送的数据量为: $$ 最小帧长度=25\mu s\times 10 \times 10^{6}=250bit=31.25byte $$
- 为了简化规范,IEEE 802.3标准规定,以太网最小帧长为64字节(包括帧头和帧尾),其中有效载荷为46字节,帧头为18字节。
注意!!::以太网协议中规定了帧间间隔 (Interframe Gap, IFG),大小为 96 比特时间。即发生碰撞后,会等待 96 比特时间发现无碰撞再继续。
随机量 \(K\) 的选择¶
- 二进制指数后退(binary exponential backoff)
- 传输一个给定帧的时候,在该帧经历了一连串的 \(n\) 次碰撞后,节点随机地从 \(\{ 0,1,2,\dots,2^{n-1}\}\) 中选择一个 \(K\) 值。因此一个帧经历的碰撞越多,其 \(K\) 选择的间隔可能越大。
- 对于以太网,一个节点等待的实际时间是 \(K\cdot 512比特时间\)(即发送 512 比特进入以太网所需时间量的 \(K\) 倍)
CSMA/CA (CSMA with Collision Avoidance)¶
| 特性 | CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) | CSMA/CD (Collision Detection) |
|---|---|---|
| 适用场景 | 无线网络(如 Wi-Fi) | 有线网络(如以太网) |
| 冲突处理方式 | 通过退避和确认机制避免冲突 | 在冲突发生后立即检测并停止传输 |
| 信道监听 | 在发送前监听信道是否空闲 | 在发送中监听是否发生冲突 |
| 冲突发生后 | 如果未收到 ACK,则重传 | 如果检测到冲突,则停止发送,进入退避机制 |
| 退避机制 | 发送前等待随机时间,减少冲突概率 | 冲突发生后等待随机时间,再重新尝试发送 |
| 冲突检测 | 无法直接检测冲突,依赖 ACK 确认 | 可以实时检测冲突 |
| 信道利用率 | 较低,因退避时间和 ACK 消耗资源 | 较高,但在高流量时可能因冲突频繁降低效率 |
| 隐藏节点问题 | 易受隐藏节点问题影响 | 无隐藏节点问题 |
| 硬件需求 | 无需特殊硬件检测冲突 | 需要硬件支持冲突检测 |
| 延迟 | 相对较高,因为增加了退避时间和 ACK 开销 | 相对较低,冲突后立刻尝试重传 |
| 典型应用 | IEEE 802.11(Wi-Fi) | IEEE 802.3(以太网) |
其和 CSMA/CD 最大的区别正如名字,一个是避免(CA),一个是监测(CD)
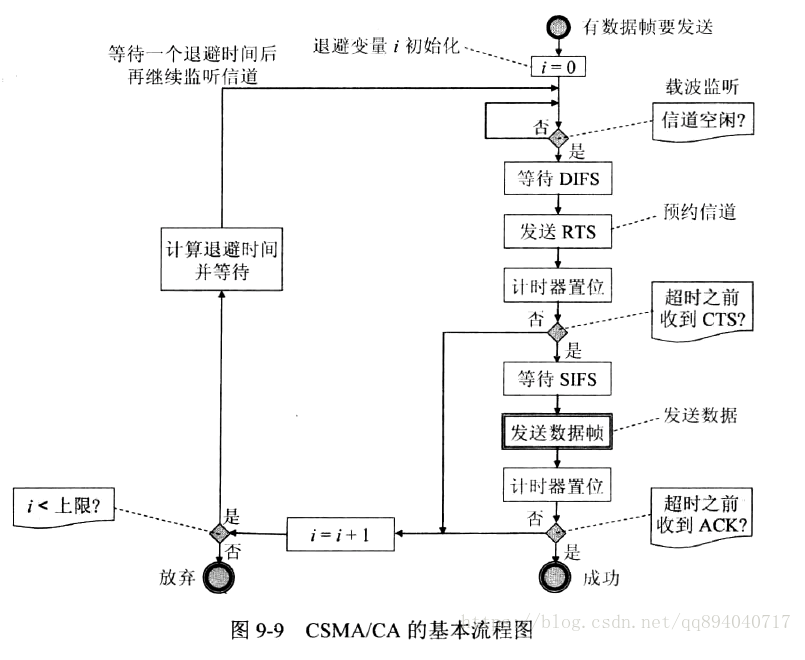
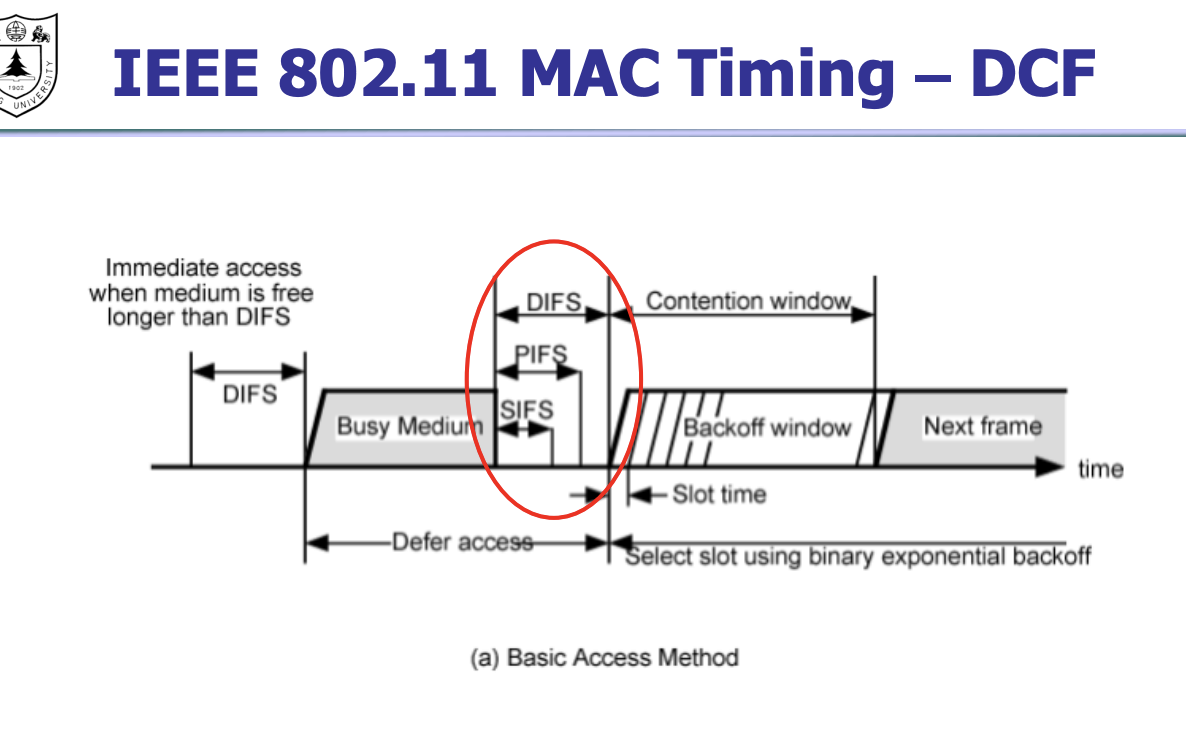
- 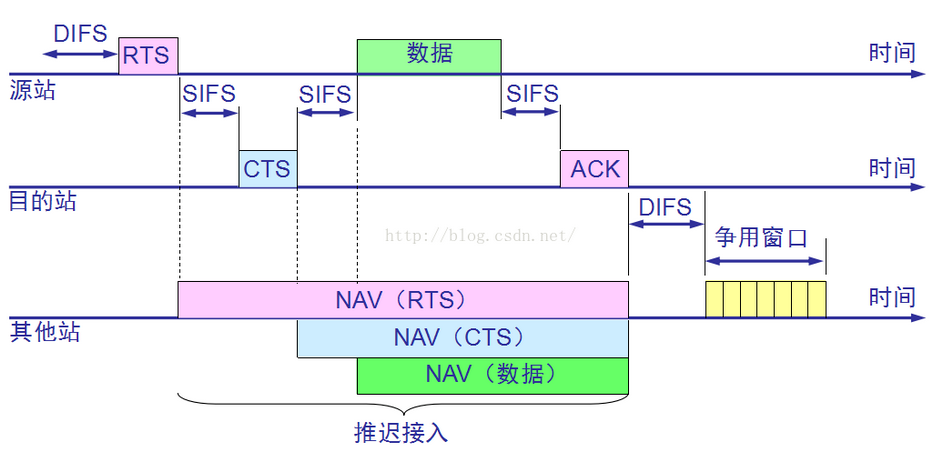 1. 若站点最初有数据要发送(而不是发送不成功再进行重传),且检测到信道空闲,在等待时间DIFS后,就发送整个数据帧。
2. 否则,站点执行CSMA/CA协议的退避算法。一旦检测到信道忙,就冻结退避计时器。只要信道空闲,退避计时器就进行倒计时。
3. 当退避计时器时间减少到零时(这时信道只可能是空闲的),站点就发送整个的帧并等待确认。
4. 发送站若收到确认,就知道已发送的帧被目的站正确收到了。这时如果要发送第二帧,就要从上面的步骤(2)开始,执行CSMA/CA协议的退避算法,随机选定一段退避时间。
5.
1. 若站点最初有数据要发送(而不是发送不成功再进行重传),且检测到信道空闲,在等待时间DIFS后,就发送整个数据帧。
2. 否则,站点执行CSMA/CA协议的退避算法。一旦检测到信道忙,就冻结退避计时器。只要信道空闲,退避计时器就进行倒计时。
3. 当退避计时器时间减少到零时(这时信道只可能是空闲的),站点就发送整个的帧并等待确认。
4. 发送站若收到确认,就知道已发送的帧被目的站正确收到了。这时如果要发送第二帧,就要从上面的步骤(2)开始,执行CSMA/CA协议的退避算法,随机选定一段退避时间。
5. 
Performance of MAC¶
Performance Metric¶
- Media Utilization (媒体利用率)
- Time used for frame transmission vs. time the shared media is occupied $$ U=\frac{{\text{Time for frame transmission}}}{\text{total time for a frame}} $$
- 这个式子的直观理解:真正传输一个 frame 的时间,占一个帧占用的总时间的比率。即链路利用率(media utilization)。
Different Networks¶
这里列出两个不同的网络组织方式 - Contention free - Point-to-Point Link - Ring LAN - Random access - ALOHA, slotted ALOHA - CSMA/CD
Point-to-Point Link with No ACK¶
仍考虑这个式子:
$$
U=\frac{{\text{Time for frame transmission}}}{\text{total time for a frame}}
$$
对于长帧 (Large frame) 和短帧 (Small frame) 我们的考虑有区别:因为 transmission time 和 propagation time 的对比不一样
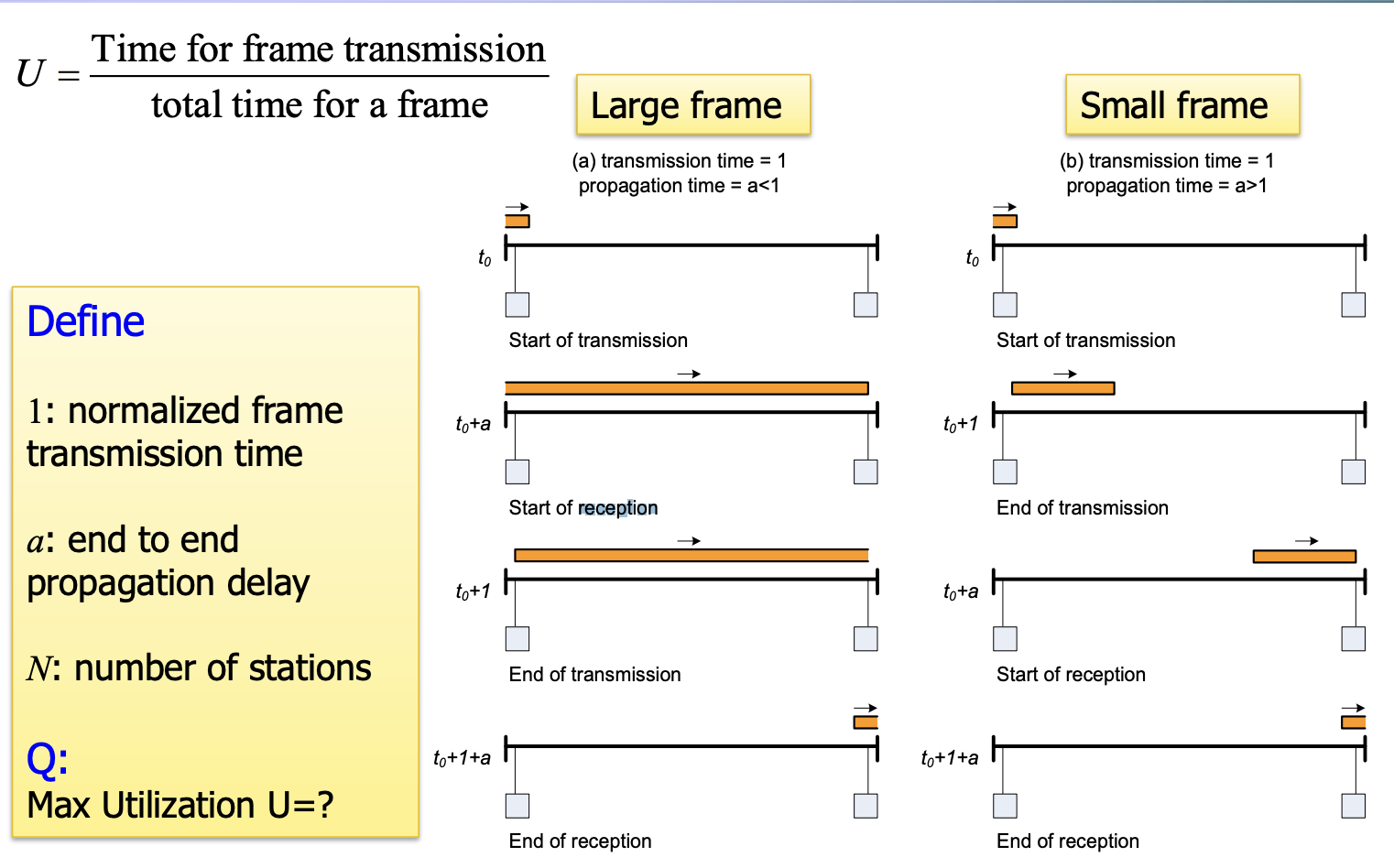
Max Utilization¶
- 给出参数和假设
- \(1\): normalized frame transmission time
- \(\alpha\): end to end propagation delay
- \(N\): number of stations
- Each station has frame to transmit
- Total frame time=
transmission delay+propagation delay= \(1+\alpha\)
- Total frame time=
所以容易推导出 $$ U=\frac{1}{{1+\alpha}} $$
MAC Address and Discovery¶
MAC Address define¶
- Medium Access Control (MAC) Address
- Numerical address associated with a network adapter
- Flat name space of 48 bits (HEX)
- Unique, hard-coded in the adapter when it is bulit
Address Configuration¶
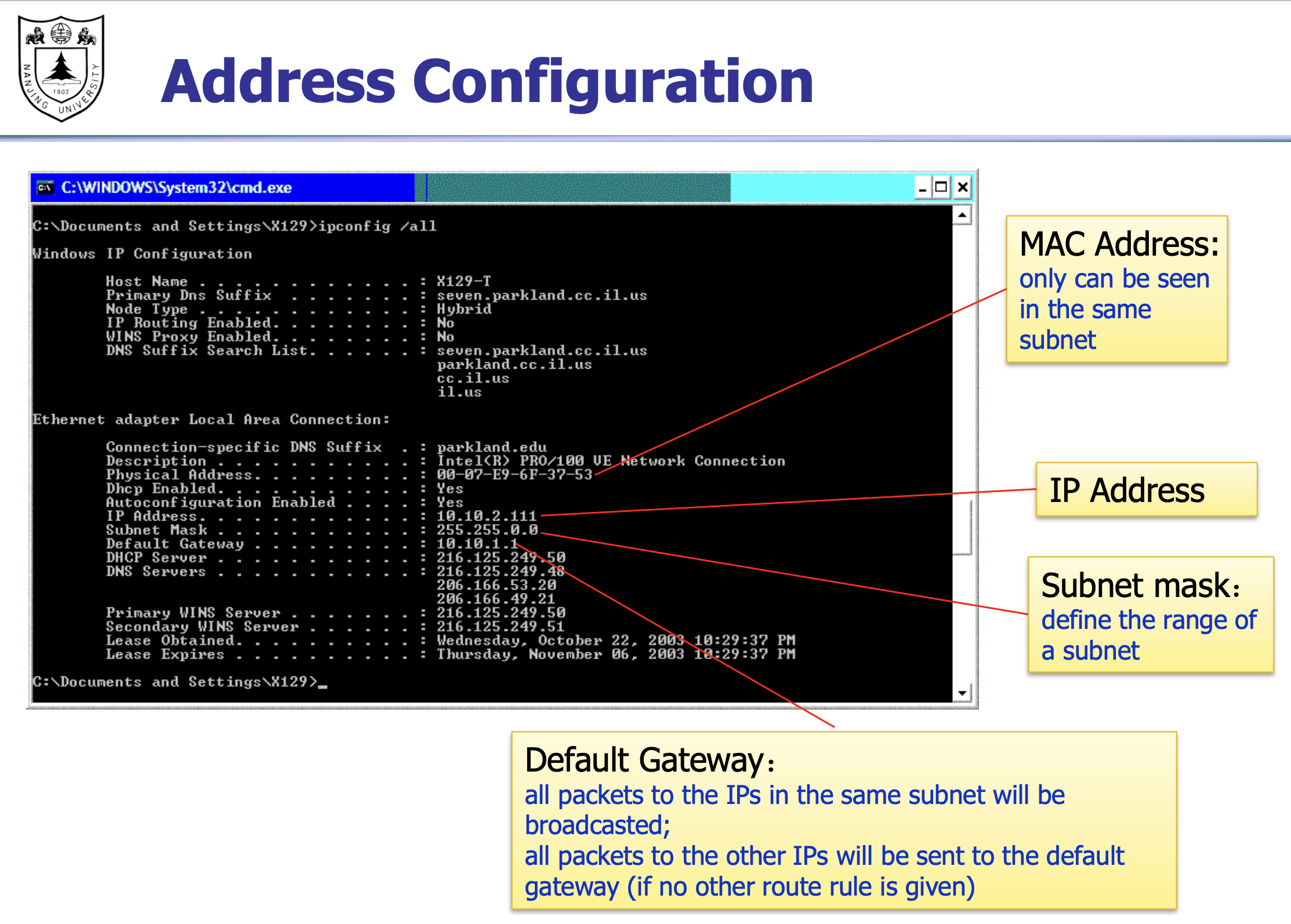
Discovery¶
一个主机(Host)诞生时候,只知道他的 MAC 地址 它在和 Host B 通信时,必须获得一系列信息 - local IP address - peer IP address - peer MAC address - first-hop router' s address? (if B is not local)
如何 Discover: ARP & DHCP¶
链路层 Link Layer 提供了发现协议 - ARP: Address Resolution Protocol - DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - Confined to a single local-area network (LAN) - Rely on broadcast capability - 这两个协议开始通信的方式都是广播
如何获得 Destination MAC¶
思考这样一个情况:A ping B,source IP, source MAC destination IP 都知道,问题是 destination MAC 呢? - On LAN, ARP is used to get a host/router's MAC given its IP address
### ARP Procedure
每个主机 host 都维护一个 ARP Table
- List of (\(\text{IP address}\to\text{MAC address}\))
Bridge¶
Why we need bridge¶
- Ability to expand beyond single LAN
-
Provide interconnection to other LANs/WANs
-
所以需要桥
- Connects LANs, usually more than two LANs
-
Identical protocols for physical and MAC layers
-
存储转发 LAN 的帧(Store, forward LAN frames)
- Switch(route)functions needed
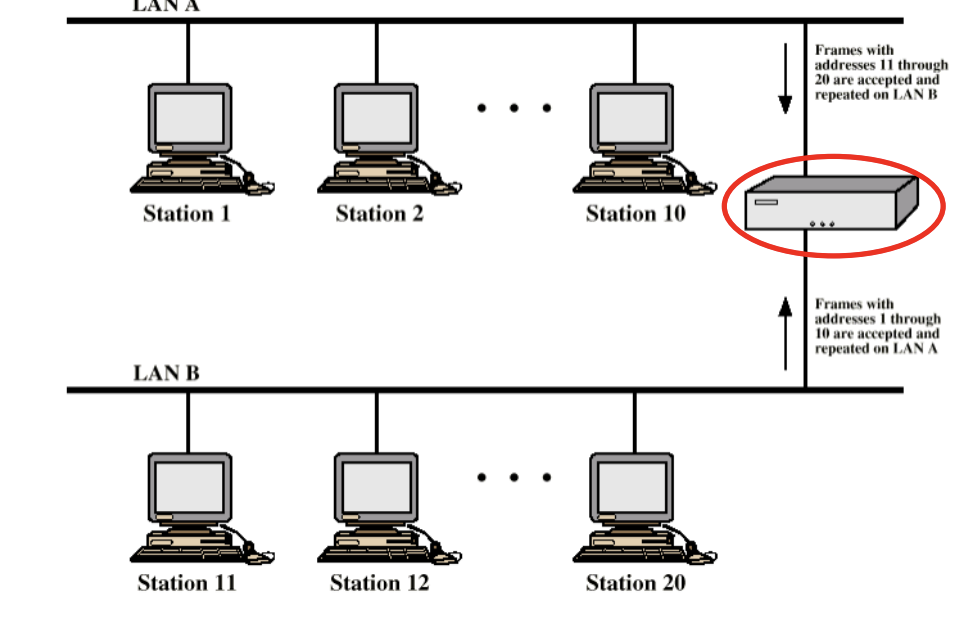
Requirements of a Bridge¶
- Store and Forward (存储转发)
- 读在一个 LAN 上传输的帧
- 先缓存这个帧,检查其正确性。
- 检查其 MAC 地址
- 选择性存储这些地址到其他 LANs (selectively store those address to other LANs)
- Using MAC protocol of second LAN, retransmit each frame
- Transparent(透明性)
- Stations are unaware of presence of bridges
- 不知道其他桥的存在
- Plug-and-play, self-learning(即插即用,自我学习)
- Bridges do not need to be configured
Bridge Protocol Architecture¶
靠 MAC 地址来做路由
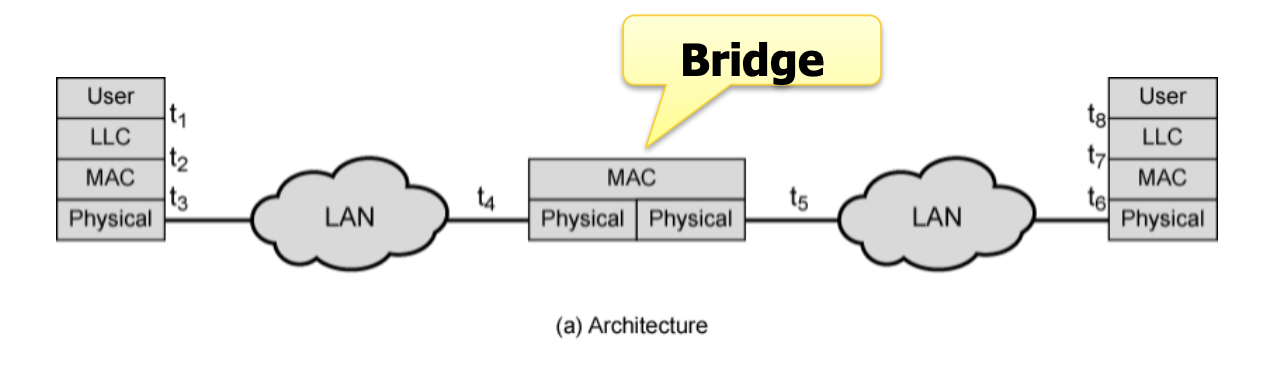 - Relaying MAC frames
- Relaying MAC frames
Broadcast Ethernet¶
基本逻辑¶
有一条广播链路 (broadcast link)
- Each receiver’s link layer passes the frame to the network layer:
- If destination address matches the receiver’s MAC address OR if the destination address is the broadcast MAC address (ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff)
- Ethernet is "plug-n-play" 即插即用
在 extended LANs 中做广播¶
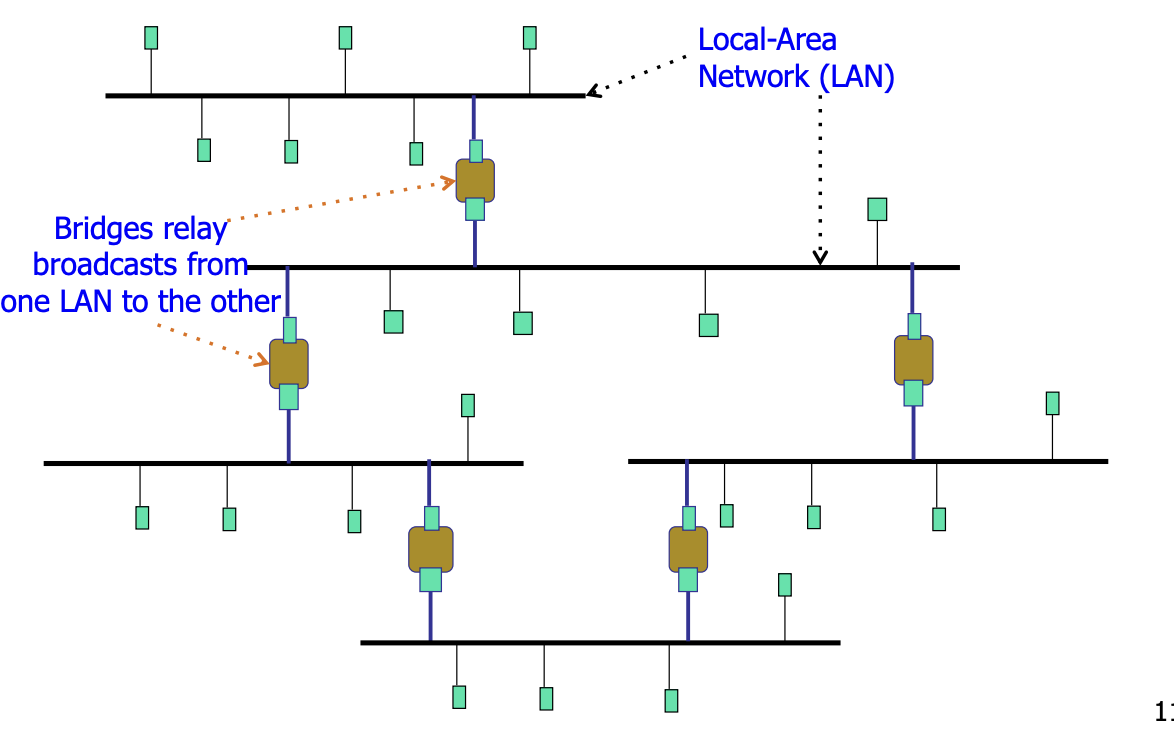
Broadcast Storm 广播风暴¶
问题介绍¶
但是当出现 环(loop)(比如上图)之后,就会出现 "broadcast storm",即相同报文被反复广播
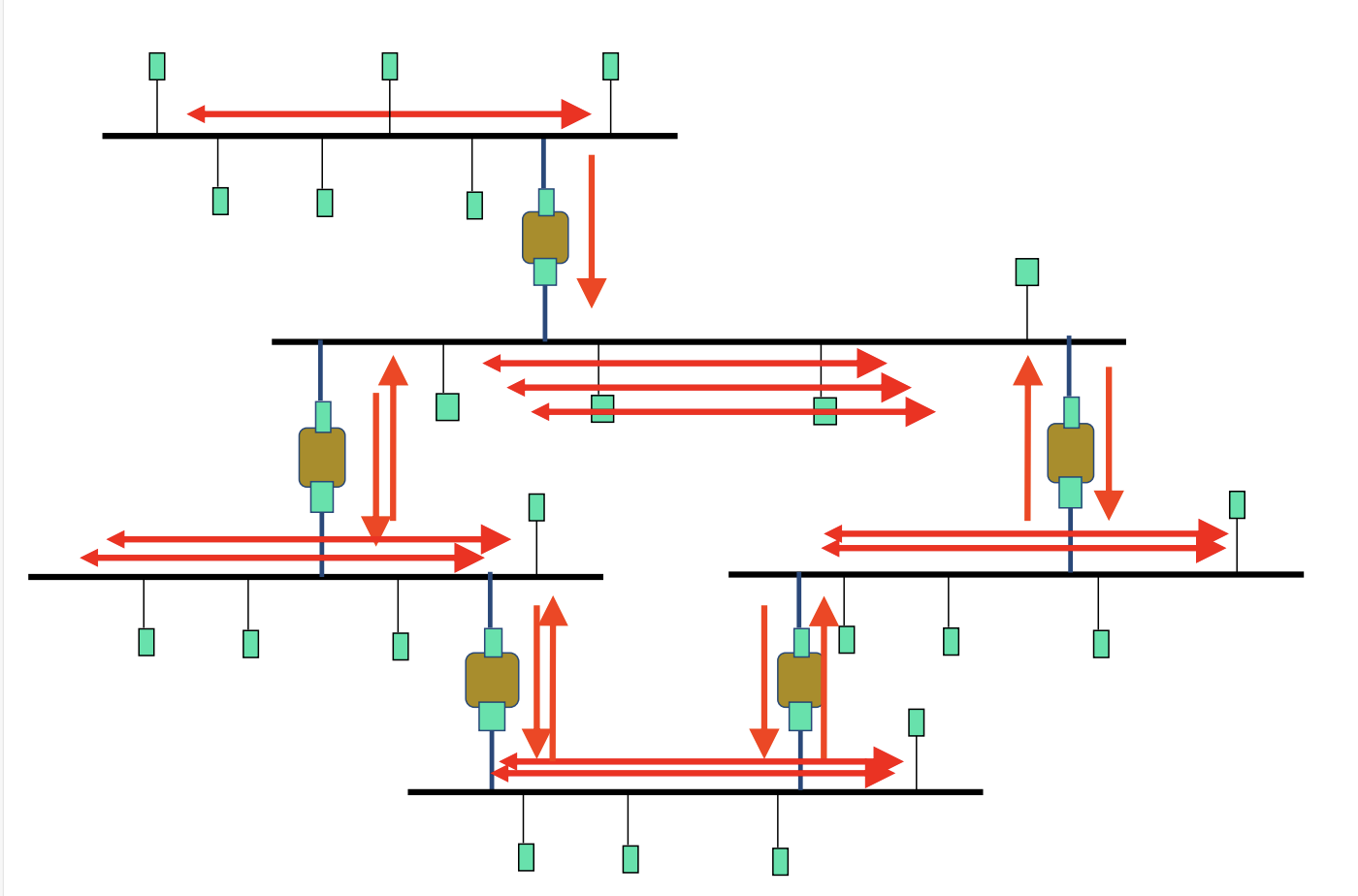
解决方案-生成树算法¶
构造一个生成树算法。因为生成树无环
具体而言,算法有两个角度
- Pick a root (选择根,即最小路径的终点)
- Destination to which shortest paths go
- Pick the one with the smallest identifier (MAC addr.)
- Compute shortest paths to the root (计算最小路径)
- No shortest path can have a cycle
- Only keep the links on shortest-paths
- Break ties in some way (so we only keep one shortest path from each node)
- Breaking ties (很形象,一个结🪢): 如果有多个最短路径到根,选择一个路径,它用到的邻居有最小的 ID
- Ethernet’s spanning tree construction does both with a single algorithm
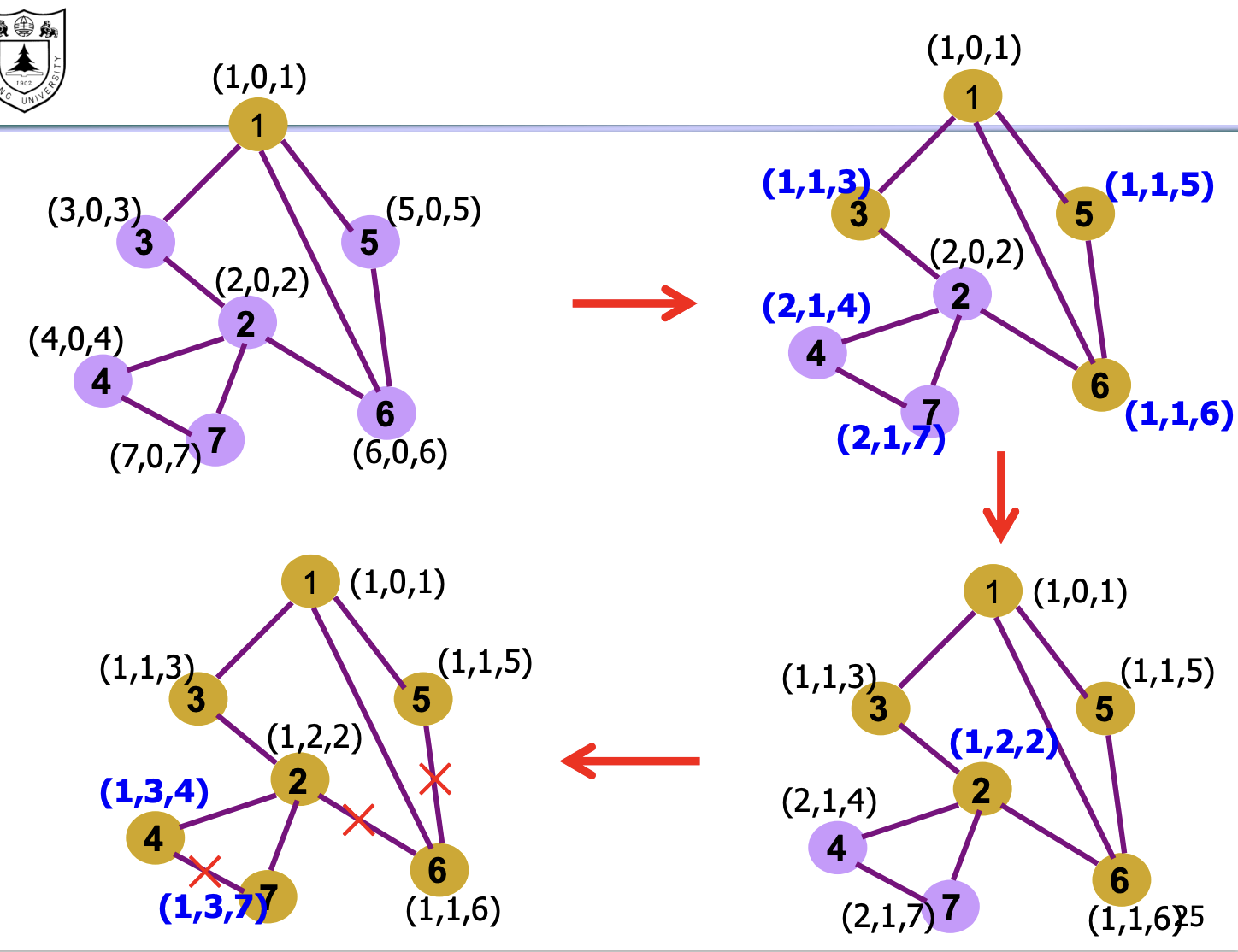
具体实现¶
我们在这里实现的实际是一个分布式算法,需要考虑: - 时间复杂度 - 报文复杂度
每个点通过报文 (Messages) 来沟通实现算法,报文结构如下
- Messages(Y,d,X)
- Proposing Y as the root
- 推举 Y 作为根
- X:标志报文的来源,From X
- d
- And advertising a distance d to Y
- 是广告一个距离 d,告诉 Y
基本逻辑是这样:
- 路由器将选择有最小的 identifier(MAC address)的节点作为根 root
- Each node determines if a link is on its shortest path to the root; exclude it from the tree if not
- 每个节点都决定,一个链接是否在它到达根的 最短路径上,如果不是,则'去掉'这条链接。
具体步骤:
- 最初,每个节点都“推举”自己是根(之后再根据各自的 MAC 更新)(proposes itself as the root)
- Switch X announces (X,0,X) to its neighbors
- Nodes update their view of the root
- 节点开始更新它们对于根的看法(及分布式的比对,最后得到 mac 地址最小的作为根)
- Upon receiving (Y,d,Z) from Z, check Y 's id
- if Y 's id < current root: set root = Y
- Nodes compute their distance from the root
- 节点计算它们到根的距离
- Add 1 to the shortest distance received from a neighbor
- 具体来说是从邻居的 d 再加上 1
- If root or shortest distance to it changed, send neighbors updated message (Y, d+1, X)
- 如果根,或到达根的最短距离发生变化,就发送
运行图:
地址学习 (Address Learning)¶
- Each bridge maintains a forwarding database
- Forwarding database can be learned
- When frame arrives at port
X, it has come from the LAN attached to portX - Use the source address to update forwarding database for port X to include that address
- Timer on each entry in database, Entry deleted when timer is off
- Each time frame arrives, source address checked against forwarding database (在通信过程中,记录地址和端口信息,分布式的)
Layer 2 Switch¶
由于工作于 OSI 模型的第二层(数据链路层),故称二层交换机(Layer 2 Switch)
仍然需要 Loop resolution
self learning¶
以太网交换机是 自学习的 具体而言: 1. 收到一个 frame,先查看 source MAC 是否在自己维护的 table 中 - 如果有,则 2 - 如果没有,则将这个地址放入 table 中 2. 检查 destination address 查表,如果有,则转发。没有,则进行 flood:flood到除了 in-port 之外的所有端口
1. record incoming link,MAC address of sending host
2. index switch table using MAC destination address
3. if entry found for destination
then {
if destination on segment from which frame arrived
then drop frame
else forward frame on interface indicated by entry
}
else flood /* forward on all interfaces except arriving interface */
Hubs(集线器)¶
- 物理的重复器 physical repeaters
- 星型结构,所有节点通过两条线连接到 hub (transmit, receive)
- 当一条线路 transmit 信息时,hub 向所有其他线路(receive)进行简单重复消息
- 速度就是单条线路的最大速率
- 连接的所有设备处于一个冲突域
Layer 3 switches¶
- involving router (路由器) functions.
- Layer 3 switchers 具有路由功能(链路层 MAC+网络层 IP)
- 硬件上引入 ip 协议,连接 2 层交换机 为什么要引入?
- 当 stations 变多,layer 2 switches 出现了不满足问题
- 共用广播 mac 地址,broadcast overload,降低了效率
- ARP,DHCP,IGMP 频繁广播
- Lack of multiple paths,不够灵活
- 共用广播 mac 地址,broadcast overload,降低了效率
- 网络层交换机
- 硬件上实现了 packet-forwarding(IP)逻辑
- 将相似的 LANs 划分成子网,用 layer 3 switcher 彼此连接。
无线网络¶
无线链路和网络特征¶
无线链路有许多独特的特点。 - 递减的信号强度,也叫做 路径损耗(pass loss) - 来自其他源的干扰,在同一频段发送的电波源将相互干扰。 - 多路径传播,电磁波的一部分受地面和物体反射,在发送方和接收方走了不同长度的路径,就出现多径传播(multipath propagation) - 半双工,无法同时发送和接受(自干扰问题难以解决) - 不适用 CSMA/CD
一些通信的衡量。
评估指标 SNR 和 BER¶
- SNR: (Signal-to-Noise Ratio, SNR) 信噪比。度量单位通常为分贝。
- BER:(Bit Error Rate)比特出错率
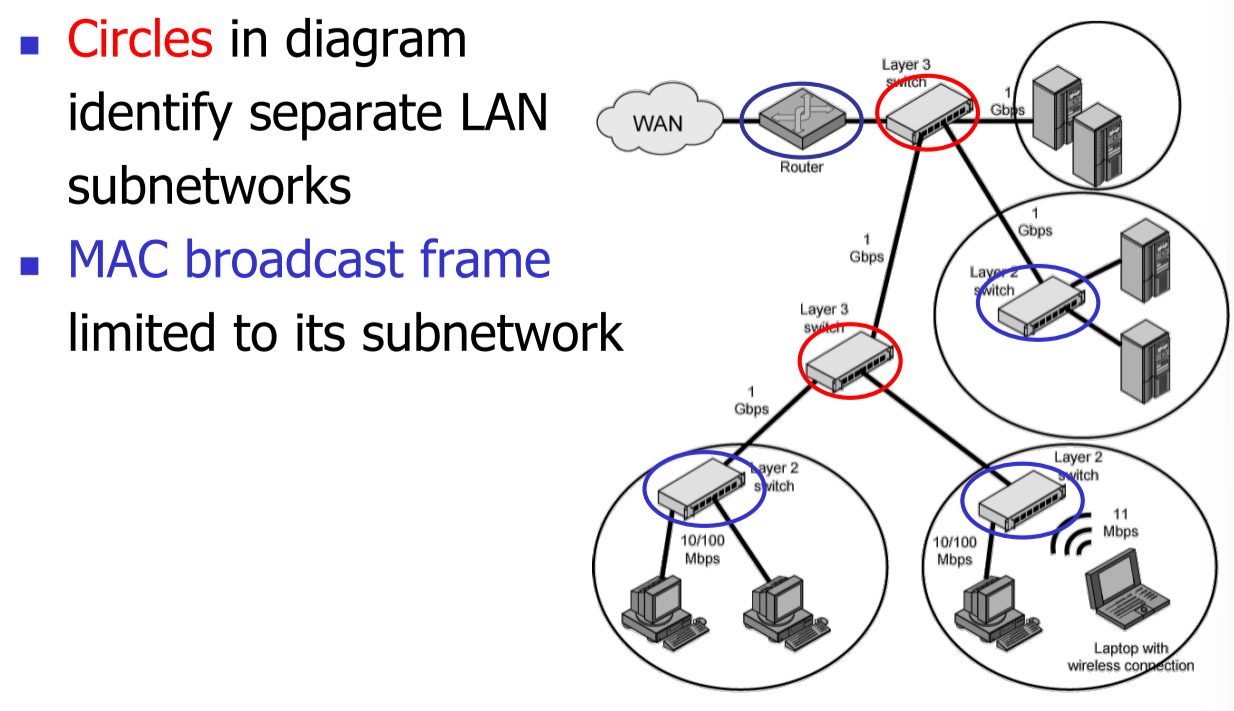
802.11无线局域网体系结构¶
-
基本构件:基本服务及(Basic Service Set, BSS)
-
接入点(Access Point, AP)**
- 即中央基站(base station)
- Extended Service Set(ESS)
- 拓展服务集
- Multiple BSSs interconnected by Distribution System (DS)
- DS can be a switch, wired network, or wireless network
- An ESS appears as a single logical LAN
- Protals (Routers) provide access to Internet
- Distribution System(DS):
- 分布系统。用于连接不同的 BSS
- A system used to interconnect a set of BSSs and integrated LANs to create an ESS
信道-关联¶
每个无线站点在能够接受/发送之前,必须和一个 AP 相关联。安装 AP - 管理员为分配一个服务集标识符 (Service Set Identifier, SSID) - 还必须为该 AP 分配一个信道号 - 是在运行频段,划分了相互重叠的 11 个信道。只有两个信道相隔够多才可以。 -
4-Frame Exchange¶
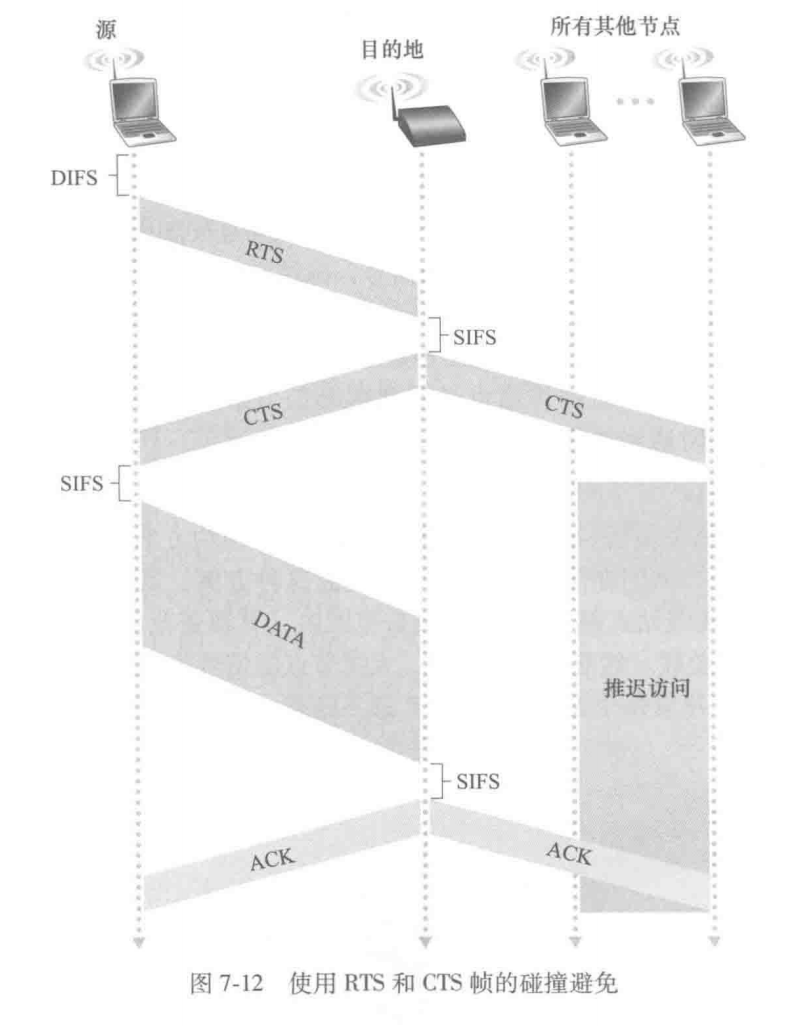
所谓 4-Frame,即 1. RTS 2. CTS 3. DATA 4. ACK
隐藏终端问题¶
必考¶
-
什么是隐藏终端?
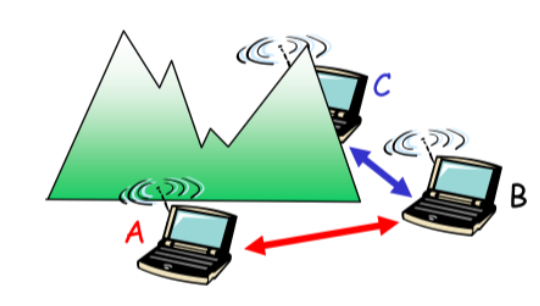
- 无线网多设备连接
- A、C 可能不知道对方的存在,同时向 B 发出信息,导致冲突干扰
- 解决:应用 4-Frame-Exchange To enhance wireless reliability, 4-frame exchange may be used
- Source issues a Request to Send (RTS) frame to destination
- Destination responds with Clear to Send (CTS) (允许发送)
- After receiving CTS, source transmits DATA
- Destination responds with ACK 整体流程是这样的:
- 发送方要发送信息:
- 向 AP 发送 RTS 帧,说明传输 DATA 帧和确认(ACK)帧需要的总时间
- AP 收到 RTS,广播一个 CTS 帧作为响应
- 发送方收到 CTS,知道可以发送
- 其他站点知道,此事件不要给这个 AP 发送
MAC 协议(Media Access Control)¶
选择了一种随机接入协议 - 带碰撞避免的 CSMA(CSMA with collision avoidance) CSMA/CA - CSMA 应该已经很熟悉了,#CSMA
详细了解 CSMA/CA 算法¶
TODO¶
流程图:
校验方法¶
奇偶校验¶
包括单校验和二维奇偶校验,参考这个题目 HW6_231275036_朱晗 - 单校验只能侦测错误,不能改正 - 二维奇偶校验可以改正一个错,发现最多两个错。
因特网校验和(Internet checksum)¶
在 UDP 协议中介绍过 UDP Checksum
流程¶
一系列 \(d\) 比特数据被当作一个 \(k\) 比特整数的序列处理。 - 简单方法:将这 \(k\) 个比特加起来,然后用得到的和作为差错检测比特 - 具体来说,数据的字节作为 16 比特的整数对待并求和。这个和的反码形成了携带在报文段首部 header的因特网检验和。 - 接收方:通过对接受的数据(包括检验和)的和取反码,并且检测其结果是否为全 1 比特来检测校验和。
循环冗余检测 (Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC)¶
基本概念¶
CRC 编码也叫做 多项式编码(polynomial code)
- 该编码将要发送的比特串看作为系数是 0 和 1 的一个多项式。
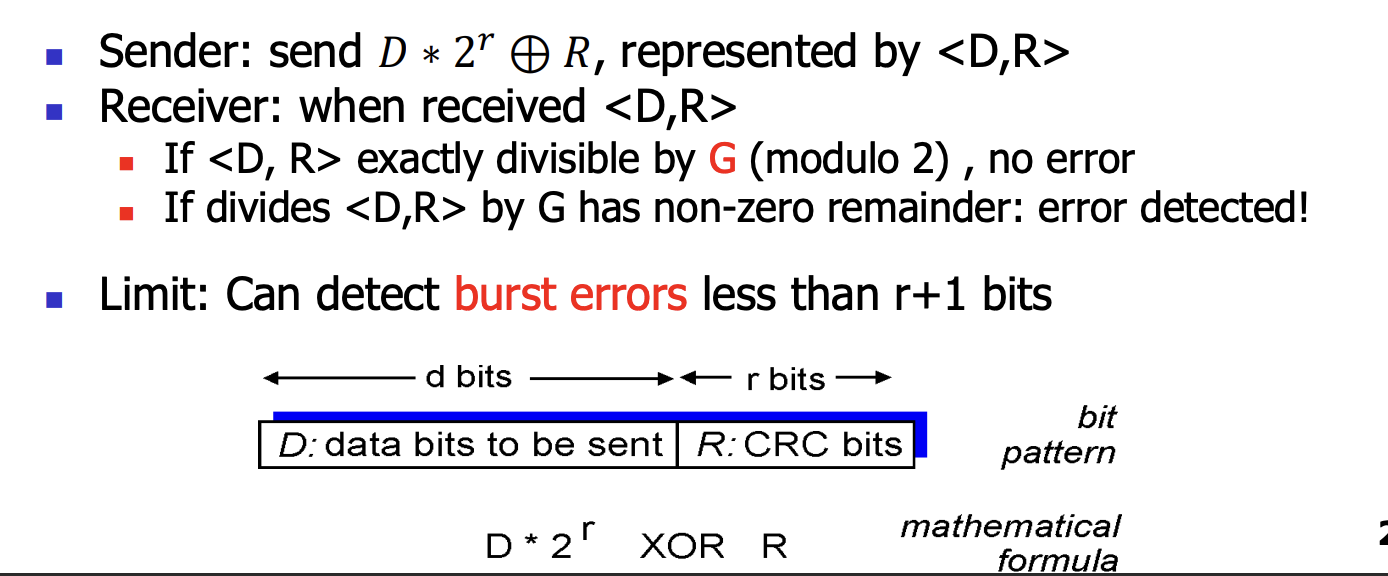
发送方和接收方协商一个 \(r+1\) 比特模式(bit pattern)
- 称为 生成多项式(generator),表示为 \(G\),要求其最高位(最左边)是 1
对于一个给定的数据段 \(D\),发送方要选择 \(r\) 个附加比特
- 这称为 \(R\),将他们附加到 \(D\) 上,然后得到的 \(d+r\) 的 bit pattern(被解释为一个二进制数, binary number)用模 2 算术恰好能被 \(G\) 整除。
- 即也就是 \(R\) 的长度是 \(G\) 的长度-1
- 检测差错:
- 接收方用 \(G\) 取除接收到的 \(d+r\) 比特。如果余数为非零,接收方知道出现了差错;否则认为数据正确而被接收。
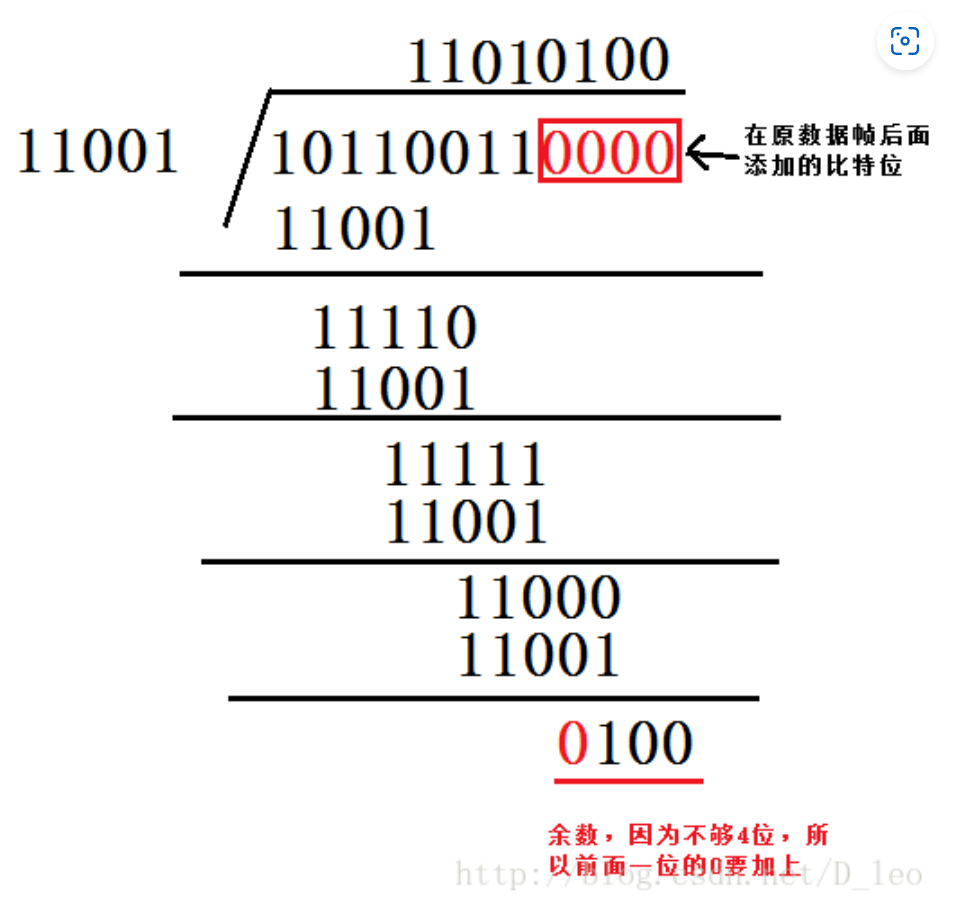
所谓模 2 算术:¶
- 模 2 除法,加法减法都不借位,相当于进行异或操作 (在计算除法的过程中),首位是0商为0,首位是1商为1
- 意思是对齐 G 位数之后,如果当前在除的数(如下面第一步除法得到的 11110)首位是 1,就商 1。否则商 0
- 与四则运算不同的是模2运算不考虑进位和借位,模2算术是编码理论中多项式运算的基础。
- 则 加法 和 减法 是一样的。且等价于异或。
- 乘法:乘以 \(2^{k}\) 就是 bit pattern 左移 \(k\) 个位置,除法等价
问题:如何找到合适的 \(R\)?¶
\(R\) 要满足:对于 \(n\) 有 其中 \(D\cdot 2^{r}\) 表达的就是在 \(D\) 的后面延伸出 \(r\) 位,用来放 \(R\)
这个等式说明,如果用 \(G\) 来除 \(D\cdot2^{r}\),余数值正好是 \(R\)(只要把 XOR 理解为和你就很容易懂了) 所以得到计算 \(R\) 的式子
越说越糊涂深化理解:- 其实取个倒数也是一样的,因为在模 2 算数中,谁除谁都是一个做异或罢了
吞吐量¶
交换机网络¶
交换机网络中的聚合吞吐量¶
定义:¶
$$ \text{聚合吞吐量} = \sum_{i=1}^N R_i $$ 其中:
-
\(R_{i}\):交换机第 \(i\) 个端口的有效数据传输速率。
-
\(N\):交换机端口的总数。
特点:¶
- 专用信道:
- 交换机为每对通信设备提供独立的通信信道,避免了碰撞。
- 每个端口的传输速率可以独立计算,无需考虑共享带宽的影响。
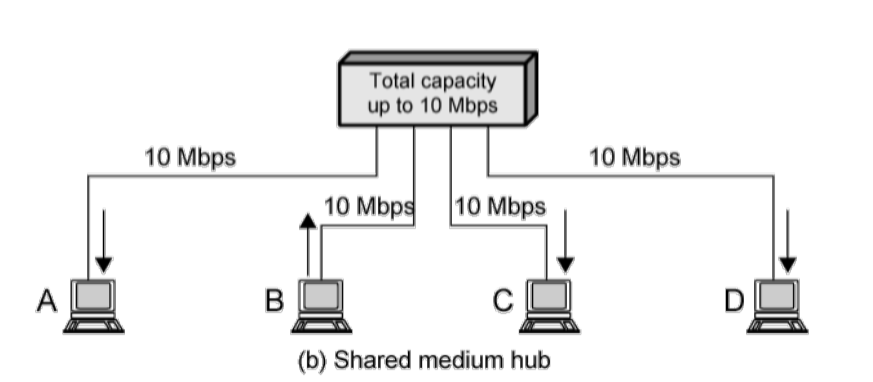
集线器网络¶
集线器网络中的聚合吞吐量¶
定义:¶
集线器的聚合吞吐量是指在单位时间内,通过集线器传输的有效数据量总和。
特点:¶
- 共享信道:
- 集线器不区分端口,所有端口的数据流共享同一个信道。
- 如果两个或多个端口同时发送数据,可能会发生碰撞。
- 半双工通信:
- 集线器只支持半双工通信,意味着在同一时刻,信道上只能有一个设备发送数据。
- 设备需要使用 CSMA/CD 协议来检测信道冲突并解决碰撞问题。
- 带宽限制:
- 集线器总带宽等于其单个信道的速率。例如,10 Mbps 的集线器,其总带宽为 10 Mbps,而非端口数的倍数。