多媒体 MultiMedia networking¶
Video¶
- 定义:
- Video: sequence of images displayed at constant rate
- Digital image: array of pixels
- each pixel represented by bits
- Coding: use redundancy within and between images to decrease # bits used to encode image
- Example:
- MPEG 1
- MPEG2
- MPEG4 (often used in Internet)
- Example:
三种应用类型¶
Streaming, stored audio video¶
- streaming: can begin playout before downloading entire file
- stored (at server): can transmit faster than audio/video will be rendered (implies storing/buffering at client)
- e.g., YouTube, Netflix
缓存技术应用
Streaming multimedia:UDP¶
- Server sends at rate appropriate for client
- often: send rate = encoding rate = constant rate
- transmission rate can be oblivious to congestion levels
- 特点:短 playout delay (2-5 secs) to remove network jitter
- error recovery:
- application-level, time permitting
- RTP: multimedia payload types
- UDP may not go through firewalls(由于是非安全协议)
HTTP¶
通过 HTTP GET 来获得多媒体文件。(一块一块的数据拿过来) - 以 TCP协议下的最大速度发送
- HTTP/TCP 更容易通过防火墙
DASH¶
- DASH:D*ynamic Adaptive Streaming over H*TTP
- 客户端是智能的,客户端决定:
- 什么时候请求块 (When to request chunk)
- 请求多大的码率。(higher quality when more bandwidth available)
VoIP:packet loss, delay¶
- interactive nature of human-to-human conversation limits delay tolerance
Internet QoS¶
为了适应实时通讯、大量客户端/服务端应用,大量图像的网站——所以必须支持 Quality of Service(QOS) within TCP/IP - In place of "best-effort" - Add traffic control to routers - Provide means of requesting QOS
两大 QoS 框架 - Integrated Services Architecture(ISA) - Differentiated Services(DS)
Integrated Services Architecture (ISA)¶
- Associate a distinguishable stream of IP packets with a flow
- With the same QOS parameters
- Identified by source and destination IP address, port numbers, protocol type (TCP or UDP)
- Unidirectional, Can be multicast
ISA Functions¶
- Routing Algorithm
- Link cost based on a variety of QOS parameters
- Routing / forwarding based on classes of flows with similar QoS
- Queuing discipline
- Priority queuing
- Multiple queues instead of one, taking account of different flow requirements
- Discard policy
- Selective discard instead of just new comings
- Reservation protocol
- RSVP, reserve resource for new flow at a given level of QOS
- Admission control
- Determines if sufficient resources are available for the flow at the requested QOS
- Traffic control database
- Parameters of traffic control
- Management agent
- Modifies the traffic control database
- Directs the admission control module to set policies
Differential Services (DS)¶
Policing¶
- 目标:限制 traffic 不超过给定的参数
- 三种常用的名词
- (long term)average rate: how many pkts can be sent per unit time
- peak rate:
- (max) burst size: max number of pkts sent consecutively (with no intervening idle)
- 在包的流(packet flow, traffic)进入网络之前,塑造它的样子
- Control the rate at which packets are sent
- Two traffic shaping algorithm
- Leaky Bucket
- Token Bucket
Leaky Bucket¶
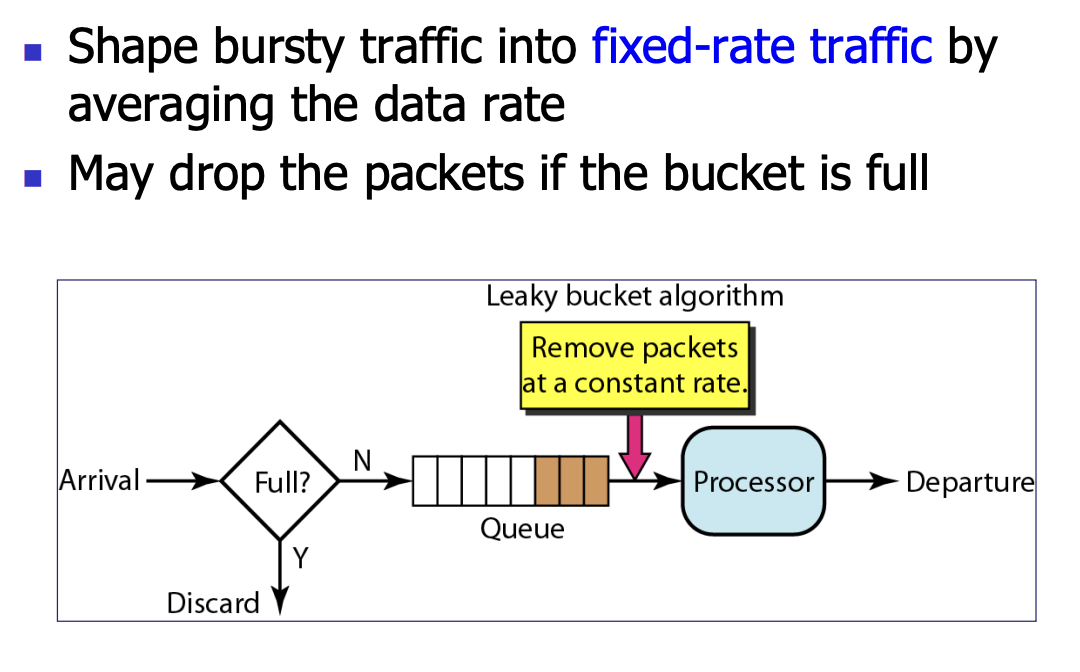
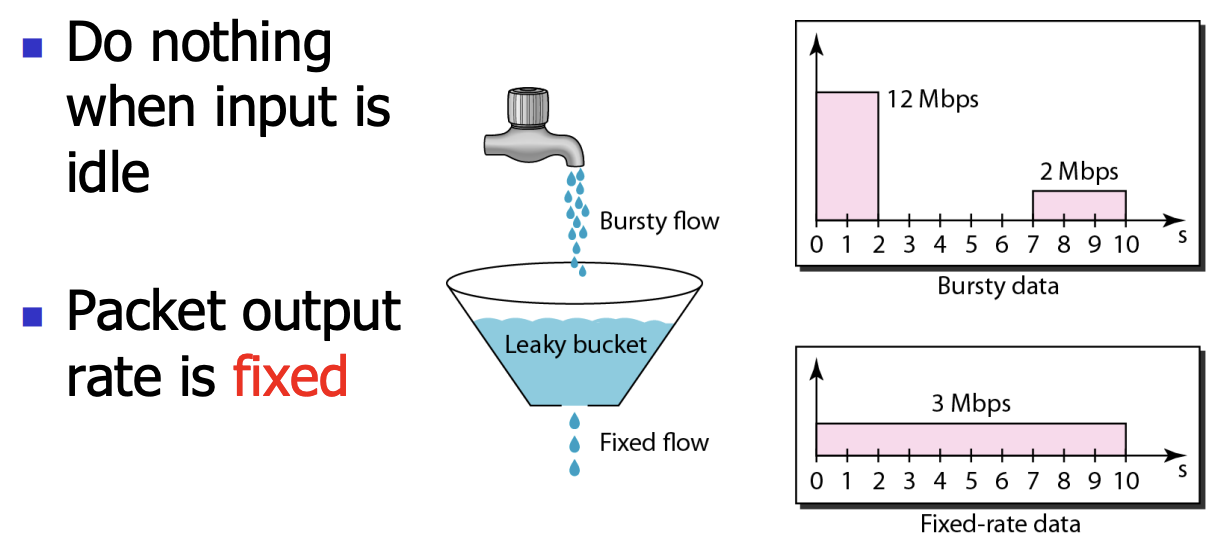 - 以恒定速率将数据放进网路,用缓存区进行稳定。
- 如果积累的数据超过了限制(超过了桶的大小),就丢包 (discard if leak)
- 起到稳定数据流的作用。
- 以恒定速率将数据放进网路,用缓存区进行稳定。
- 如果积累的数据超过了限制(超过了桶的大小),就丢包 (discard if leak)
- 起到稳定数据流的作用。
Token Packet¶
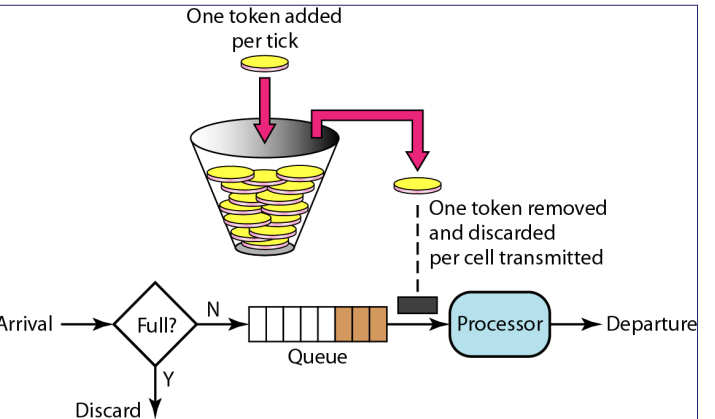
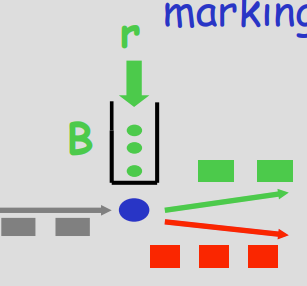
- 在边缘有一个“桶”里面装用来提供特殊服务的 token,装入速率 \(r\) 表示允许的最大(平均)速率,大小 \(b\) 表示可以爆发传输的最大数据量,没有 token 的意味着普通服务(低优先级)
- 只有持有 token,才能做
- \(t\) 时间内最多 \(rt+b\)
1. 平均速率¶
- 定义:流量在较长时间内的平均速率。
- 控制方式:通过 令牌生成速率 \( r \) 控制。
- 每秒生成 \( r \) 个令牌,表示系统允许的长期流量速率为 \( r \)。
- 如果输入流量超过 \( r \),多余的数据将被延迟或丢弃。
公式: $$ r_{\text{avg}} = r $$
2. 峰值速率¶
- 定义:短时间内流量可能达到的最大速率。
- 控制方式:通过 流出速率 \( r_{\text{peak}} \) 控制。
- 当漏桶允许以高于 \( r \) 的速率发送流量时,峰值速率由流出速率决定。
- 在串联两个漏桶时,第二个漏桶的令牌生成速率可作为峰值速率的限制。
公式: $$ r_{\text{peak}} = \min(r, \text{桶流出速率}) $$
3. 突发长度¶
- 定义:系统能够容忍的一次性最大数据量。
- 控制方式:通过 桶容量 \( B \) 控制。
- 如果桶中累积了大量令牌,可以短时间内发送这些令牌对应的数据,从而形成突发。
- 突发长度 与 \( r \) 和 \( B \) 的关系为: $$ b_{\text{max}} = B $$
突发持续时间 \( \Delta T_{\text{burst}} \)¶
突发持续时间取决于桶容量和生成速率: $$ \Delta T_{\text{burst}} = \frac{B}{r} $$
综合公式与作用¶
- 平均速率:由 令牌生成速率 \( r \) 控制。
- 峰值速率:由 流出速率 \( r_{\text{peak}} \) 控制。
- 突发长度:由 桶容量 \( B \) 控制。
示例¶
假设漏桶的参数为: - 令牌生成速率 \( $r = 10 \, \text{Mbps}$ \); - 桶容量 \( $B = 50 \, \text{KB}$\); - 流出速率 \( $r_{\text{peak}} = 20 \, \text{Mbps}$ \)。
则: - 平均速率:\($r_{\text{avg}} = 10 \, \text{Mbps}$ \); - 峰值速率:\($r_{\text{peak}} = 20 \, \text{Mbps}$ \); - 突发长度:\(b_{\text{max}} = 50 \, \text{KB}\); - 突发持续时间: $$ \Delta T_{\text{burst}} = \frac{50 \, \text{KB}}{10 \, \text{Mbps}} = 40 \, \text{ms} $$